How Can Companies Be More Resilient in the Face of Ransomware Threats?
Ransomware is no longer an abstruse trend. It has become a widely abused tactic to threaten businesses and extort ransom. Adding fuel to the fire is the COVID-19 pandemic that has enfeebled organizational security while the companies went pillar to post to embrace remote working.
The increased level of fears and anxiety among employees have further fanned the flames of the attack. Off-late, we are witnessing more companies falling prey to ransomware and the cybercriminals are walking away with millions worth of bitcoins.
Indeed, ransomware attacks have gained such worldwide notoriety that, in June 2021, American President Joe Biden declared ransomware as an escalating and shared global threat. He emphasized the need for a collective response from public and private sectors to ward off ransomware attacks.
Before exploring how companies can safeguard themselves, it’s imperative to understand what ransomware is and why it’s the malware of choice amongst cybercriminals. Let’s dive in.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a nefarious malware that restricts or limits users of a targeted organization from accessing their IT systems until the ransom is paid. However, there is no guarantee of regaining system access even after the ransom is paid. In a manner of speaking, it is a costly gamble which may have ramifications on the company’s future.
The malicious software prevents access to user systems typically in three ways:
- User file encryption
- User screen lockdown
- Remote access and control of victim’s system
Also Read: Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack
What is the Source of Ransomware?

Phishing emails are the most common source of ransomware. Upon clicking the malicious links or attachments in the phishing email, the malware corrupts the user’s system or control server.
Once the malware is inside, the malicious program spreads all over the networked systems and encrypts the data. Then, the compromised system displays a ‘ransom note’ demanding payment in exchange for the decryption key. Otherwise, attackers threaten of dire consequences.
Ransomware can also seep into your system through an exploit kit that leverages a security vulnerability in the servers. WannaCry is an example of such ransomware attack that infiltrated hundreds of systems worldwide through a gaping security hole in the Microsoft Windows OS in 2018.
The ransomware is also passed off as software update which once installed by the unsuspecting users wreaks havoc upon the system.
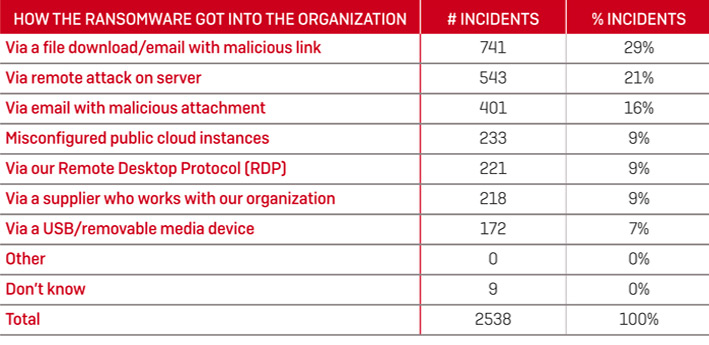
According to ‘The State of Ransomware 2020’ report by Sophos, phishing emails with malicious attachments account for 29%, and remote attacks on servers account for 21% of ransomware attack techniques.
How Do Ransom Payments work?
Often, ransomware criminals demand ransom in the form of cryptocurrency or gift cards. However, the payment doesn’t ensure that the victim will regain access. If the victim pays the ransom, the attackers could provide the decryption key.
Sometimes, the attackers don’t provide the decryption key even after receiving the payment, which results in both data and financial loss for the victim. In certain attacks, the targeted company relied on data backups and system rebuilds to restore their IT operations and chose not to pay the ransom.
According to the aforementioned report,
- 26% of ransomware victims paid the ransom and got their data back
- 56% got their data back via backups without paying the ransom
- 1% paid the ransom but didn’t get their data back
Also Read: JBS Ransomware Attack
Types of Ransomware Attacks
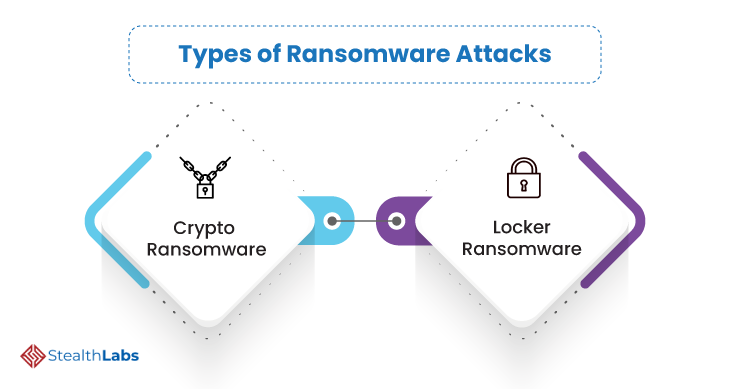
There are two prominent types of ransomware, and both are intended to attack businesses for financial gain. They are:
1) Crypto Ransomware restricts access to data or files by encrypting them with a randomly generated symmetric key. Then, the symmetric key is encrypted with a public asymmetric key. The malicious actors then demand ransom in exchange for the asymmetric key.
2) Locker Ransomware locks the system and prevents users from logging in. This malware doesn’t actually encrypt the files on the system. However, access lockout is distressing enough to compel the aggrieved to consider the ransom demand.
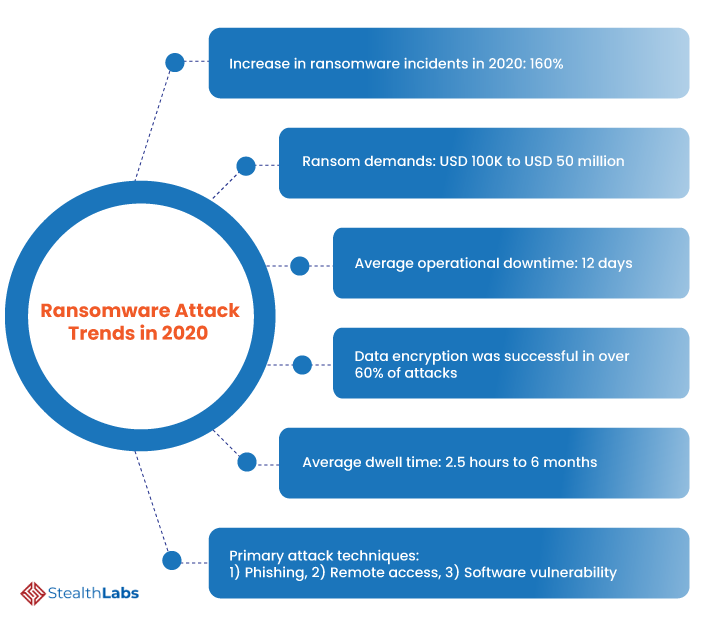
Ransomware Attack Trends in 2020
High-profile Ransomware Attacks in 2021
Within the first half of 2021, the world has already witnessed quite a few high-profile ransomware attacks. Just six ransomware groups, including REvil and DarkSide, have compromised around 292 organizations and profited more than USD 45 million in ransom.
Here are some of the most high-profile ransomware attacks that made headlines in 2021:

Stepping up the Game: Emerging Technologies, The Undesired Boons for Attackers
- 5G and IoT
Cybercriminals are leveraging IoT and 5G technologies to perpetuate their attacks. IoT devices and 5G networks increase an organization’s threat surface, unwittingly facilitating malicious actors with more entry points into an organization. Additionally, as IoT devices gather massive amounts of detailed, sensitive data, ransomware attacks targeting these devices could be more disruptive.
- Quantum Computing
Quantum computing techniques can potentially ease the decryption of data encrypted with current encryption methods, such as Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). Should ransomware attackers ever gain access to quantum computers, they can potentially decrypt systems within hours or even in seconds. The decrypted networks and systems will be at the mercy of the criminals.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Ransomware actors are leveraging AI, and its offshoot, machine learning, to conduct more automated, severe, and coordinated attacks. For instance, AI and ML can be exploited to glean personal information from social media sites and automatically compile phishing emails and malicious posts. Cybercriminals also harness these technologies to inject malicious code into benign applications and develop malware capable of imitating trusted system components.
Also Read: Kaseya Ransomware Attack
Ransomware is Real – How Can Companies Prevent the Inevitable?
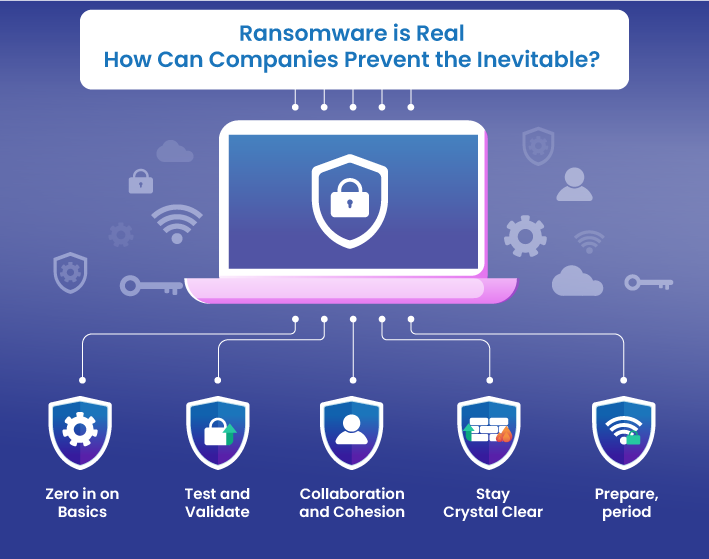
As desperate times call for desperate measures, one must consider operating under the assumption that you are already being targeted. Without further ado, focus on building cyber resilience across the business value chain.
From that position, organizations must consider the following key steps that help prevent ransomware attacks:
1) Zero in on Basics
It goes without saying that organizations must maintain good cybersecurity hygiene. You must implement robust security controls, continue patching, and ensure the protection of critical data. In addition, deploy a holistic backup and recovery strategy across the business ecosystem. Ensure you have a cyber incident response plan that’s on par with the ransomware attack trends. Look into some basic tips to prevent ransomware attacks and secure your business.
2) Test and Validate
Increase cyber confidence across the organization by continuously testing and validating your security defenses. Make sure that you have adequate visibility and coverage across your organization’s attack surface. Leverage tooling, controls, and telemetry to fortify your defense posture. Moreover, train employees regularly about the security protocols.
3) Collaboration and Cohesion
CISOs alone cannot shoulder the burden. Ensure collaboration between C-suite executives, legal experts, and external service providers like StealthLabs, so everyone knows how to work cohesively during an event. Regularly communicate with senior management, incident response partners, and third-party legal counsel to enhance support. In addition, conduct crisis management and real-time exercises to test relationships.
4) Stay Crystal Clear
Always strive for business continuity. Know how to backup and restore data at speed and scale. Be clear on incident response policies and procedures, for the response playbook is often the first thing you need after a breach.
5) Prepare, period
Ransomware is evolving, and so should you. Constantly evaluate and improve cyber resilience. Businesses evaluate their profit and loss or liquidity levels frequently, cybersecurity should be no different.
You’ve Been Hit, What To Do Next?
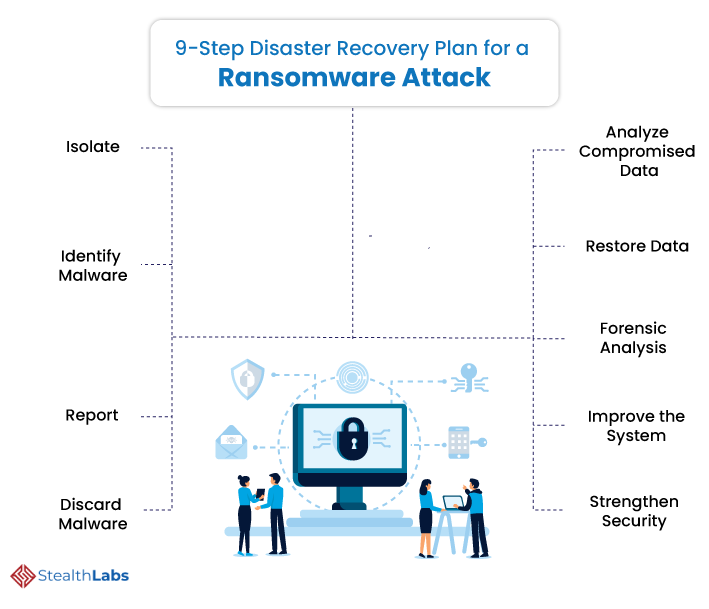
It’s a chilling moment. Critical files on your computer, and probably on the network, have been encrypted. They’ve effectively been taken hostage in a ransomware attack. So, what next?
When your organization falls victim to a ransomware attack, you need a disaster recovery plan to mitigate the impact of the incident. A typical incident response comprises the following steps:
1) Isolate: Quarantine the compromised system from the network. Shut down the device, detach the network cable, and switch off the internet connection to localize the attack.
2) Identify Malware: Then, identify the type of malware that has attacked the system. It is wise to rope in third-party security experts like StealthLabs to analyze and identify the threat.
3) Report: It is imperative to report the breach to the appropriate authorities. They can offer expertise and insights the internal security team perhaps lacks.
4) Discard Malware: Uninstall everything on the infected device and reinstall the OS.
5) Analyze Compromised Data: Identify data that the attackers have encrypted. Also, scope out the network for data exfiltration.
6) Restore Data: After containing the attack, restore data from the most recent backup available.
7) Forensic Analysis: Conduct forensic analysis of all IT environments for potential entry points. Cybercriminals often leave a back door in each system they infect.
8) Improve the System: Identify how the malicious actor breached the system and make improvements to prevent the same attack from happening again.
9) Strengthen Security: Remediate identified security vulnerabilities, updates OS, improve cyber hygiene, enhance threat detection and response operations, and drive the necessary behavioral changes required to fortify defense posture.
Capping It Off

Profitability, and of course fast payout, make ransomware a lucrative tactic that’s unlikely to wane in notoriety. While critical infrastructure companies will continue to be the prime targets, SMBs with sensitive data may increasingly find themselves in the crosshairs of criminals.
Ransomware can be challenging to combat, but prevention is best remedy for this attack. With a combination of good cyber hygiene, proactive incident response planning and employee training, an organization can steer clear of ransomware.
However, keeping up with the pace of sophistication of ransomware attacks can be a tough row to hoe. Opting for a security service provider like StealthLabs should be your path of least resistance. Reach out to us to be ransomware resilient.
More Articles:
- How small businesses can fend off cyber attacks
- Autonomous Car Security: Adversarial Attacks Against New Mobility!
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR): Overview and Importance
- Cybersecurity in Education: 10 Important Facts and Statistics
- 20 Alarming Insider Threats Statistics