Corporate Espionage, Business Disruption, or Financial Gain. Whatever the motivation, cybersecurity threats have become pervasive and continue to upend every facet of the digital realm.
According to Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), 86% of cybersecurity breaches were financially motivated, and 10% were motivated by espionage.
Beyond causing severe financial damage, cyberattacks can lead to regulatory penalties, lawsuits, reputational damage, and business continuity disruptions.
No business and IT organization are safe in the present cyber world. As cybercriminals increasingly rely on sophisticated technologies, organizations often feel hopeless as their confidential data and critical assets fall prey to malicious attacks.
Moreover, the rapid adoption of emerging technologies, including AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, have added new cyber threats for organizations while adding complexity to existing risks.
What is a Cybersecurity Threat?
A cybersecurity threat is a malicious and deliberate attack by an individual or organization to gain unauthorized access to another individual’s or organization’s network to damage, disrupt, or steal IT assets, computer networks, intellectual property, or any other form of sensitive data.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
While the types of cyber threats continue to grow, there are some of the most common and prevalent cyberthreats that present-day organizations need to know. They are as follows:
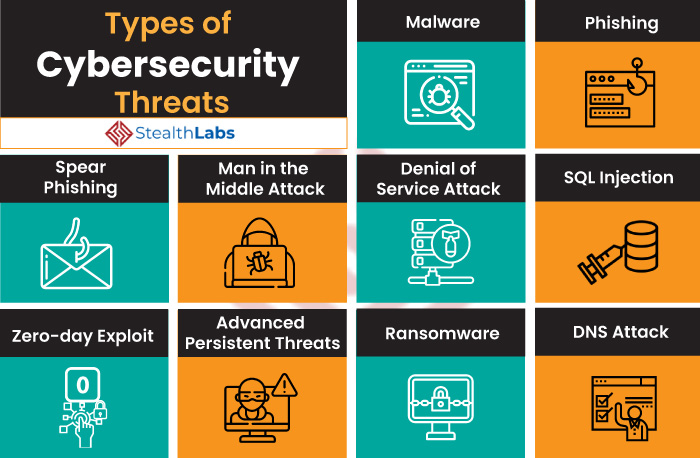
1) Malware
Malware attacks are the most common type of cyberattack. Malware is defined as malicious software, including spyware, ransomware, viruses, and worms, which gets installed into the system when the user clicks a dangerous link or email. Once inside the system, malware can block access to critical components of the network, damage the system, and gather confidential information, among others.
According to Accenture, the average cost of a malware attack is USD 2.6 million.
2) Phishing
Cybercriminals send malicious emails that seem to come from legitimate resources. The user is then tricked into clicking the malicious link in the email, leading to malware installation or disclosure of sensitive information like credit card details and login credentials.
Phishing attack accounts for over 80% of reported cyber incidents.
3) Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a more sophisticated form of a phishing attack in which cybercriminals target only privileged users such as system administrators and C-suite executives.
More than 71% of targeted attacks involve the use of spear phishing.
4) Man in the Middle Attack
Man in the Middle (MitM) attack occurs when cyber criminals place themselves between a two-party communication. Once the attacker interprets the communication, they may filter and steal sensitive data and return different responses to the user.
According to Netcraft, 95% of HTTPS servers are vulnerable to MitM.
5) Denial of Service Attack
Denial of Service attacks aims at flooding systems, networks, or servers with massive traffic, thereby making the system unable to fulfill legitimate requests. Attacks can also use several infected devices to launch an attack on the target system. This is known as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
The year 2019 saw a staggering 8.4 million DDoS attacks.
6) SQL Injection
A Structured Query Language (SQL) injection attack occurs when cybercriminals attempt to access the database by uploading malicious SQL scripts. Once successful, the malicious actor can view, change, or delete data stored in the SQL database.
SQL injection accounts for nearly 65.1% of all web application attacks.
7) Zero-day Exploit
A zero-day attack occurs when software or hardware vulnerability is announced, and the cybercriminals exploit the vulnerability before a patch or solution is implemented.
It is predicted that zero-day attacks will rise to one per day by 2021.
8) Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
An advanced persistent threat occurs when a malicious actor gains unauthorized access to a system or network and remains undetected for an extended time.
45% of organizations feel that they are likely to be the target of an APT.
9) Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware attack in which the attacker locks or encrypts the victim’s data and threatens to publish or blocks access to data unless a ransom is paid.
Ransomware attacks are estimated to cost global organizations USD 20 billion by 2021.
10) DNS Attack
A DNS attack is a cyberattack in which cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in the Domain Name System (DNS). The attackers leverage the DNS vulnerabilities to divert site visitors to malicious pages (DNS Hijacking) and exfiltrate data from compromised systems (DNS Tunneling).
The average cost of a DNS attack stood at USD 924,000 in 2020.
Sources of Cybersecurity Threats
In order to respond effectively to a cyberattack, it’s imperative to know the threat actors and understand their tactics, techniques, and procedures.
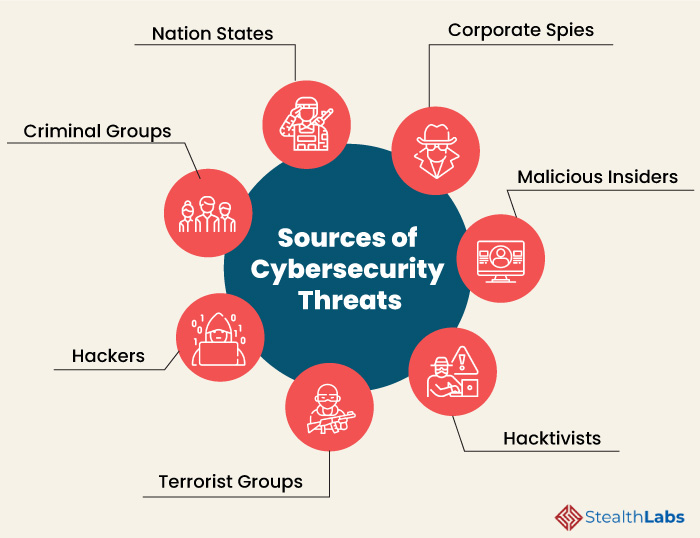
Here are some of the common sources of cyber threats:
1) Nation States
Cyber attacks by a nation can inflict detrimental impact by disrupting communications, military activities and everyday life.
2) Criminal Groups
Criminal groups aim to infiltrate systems or networks for financial gain. These groups use phishing, spam, spyware, and malware to conduct identity theft, online fraud, and system extortion.
3) Hackers
Hackers explore various cyber techniques to breach defenses and exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system or network. They are motivated by personal gain, revenge, stalking, financial gain, and political activism. Hackers develop new types of threats for the thrill of challenge or bragging rights in the hacker community.
4) Terrorist Groups
Terrorists conduct cyber attacks to destroy, infiltrate, or exploit critical infrastructure to threaten national security, compromise military equipment, disrupt the economy, and cause mass casualties.
5) Hacktivists
Hacktivists carry out cyberattacks in support of political causes rather than financial gain. They target industries, organizations, or individuals who don’t align with their political ideas and agenda.
6) Malicious Insiders
Insiders can include employees, third-party vendors, contractors, or other business associates who have legitimate access to enterprise assets but misuse that accesses to steal or destroy information for financial or personal gain.
7) Corporate Spies
Corporate spies conduct industrial or business espionage to either make a profit or disrupt a competitor’s business by attacking critical infrastructure, stealing trade secrets, and gaining access.
Top Cyber Threat Facts, Figures, and Statistics
Cyber threats continue to evolve, causing trillions worth of losses to the cyber world. Here are some alarming facts, figures, and statistics on the latest cybersecurity threats:
- The global average cost of a data breach is USD 3.92 million
- Estimated annual losses through cyberattacks to reach USD 6 Trillion by 2021
- Cybercrime breaches to increase by 76% by 2024
- Over 50% of all global data breaches to occur in the United States by 2023
- The average cost of a data breach to a US company is USD 7.91 million
- The average number of days to identify an incident in 2019 was 206 days
- 2 billion records were exposed due to data breaches in the first half of 2019
- A business will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 11 seconds in 2021
- Cyberattacks on IoT devices increased by 300% in 2019
- Cyberthreat complaints increased by 400% in the US amid the coronavirus pandemic
Emerging Cyber Threats in 2021 and Beyond
The coronavirus pandemic emerged as the biggest challenge for businesses and IT organizations in 2020. Amid the pandemic, the cyber threats and data breaches have grown in sophistication and volume, with the number of breaches increasing 273% in the first quarter, compared to 2019. According to Microsoft, the pandemic-related phishing and social engineering attacks have skyrocketed to 30,000 per day in the US alone.
What should we expect in 2021?
Here are some of the emerging cybersecurity threats that will dominate the cybersecurity landscape in 2021 and beyond:
1) Pandemic-related Attacks
The cybercriminals will continue to leverage the coronavirus pandemic and related topics as themes for their phishing and social engineering campaigns. Their attacks often coincide with significant events, such as a sudden surge in COVID-19 cases or the announcement of a new vaccine. The threat actors lure users into clicking a malicious link or attachment disguised as legitimate COVID-19 related topics.
2) Ransomware Attacks
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, businesses will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 11 seconds in 2021, down from every 14 seconds in 2019. The estimated cost of ransomware, including the cost to restore and mitigate following an attack, will cross USD 20 billion in 2021.
3) Cloud Breaches
As more companies migrate to the cloud to facilitate remote working and ensure business continuity, cybercriminals are following the same trend and targeting the cloud more frequently. Cloud-based security risks, including cloud misconfigurations, incomplete data deletion, and vulnerable cloud-apps, will be the common sources of cyberattacks.
4) Mobile Security Threats
In a bid to ensure business continuity amid the pandemic, almost all businesses initiated work from home facility. Employees working remotely use devices such as smartphones and tablets that are not properly secured, patched, and managed by the IT security department. Unfortunately, they bring some unique IT security threats and vulnerabilities, putting the organization at the risk of a cyberattack.
5) IoT Attacks
Global organizations are increasingly deploying IoT devices and applications to accelerate operations, capture more data, remotely manage infrastructure, improve customer service, and more.

However, many IoT devices often lack robust security features, putting them at risk of cyberattack. Cybercriminals can leverage the IoT vulnerabilities to gain control of devices for use in botnets and penetrate the network.
Also Read: Cyber Attacks and Data Breaches in 2020
As cybercriminals continue to adopt new technologies and attack strategies, organizations must adapt their approach to cybersecurity. Below are some cybersecurity best practices that help your organization prepare against cyber threats and ensure business continuity:
Cybersecurity Best Practices to Protect from Cyber Threats
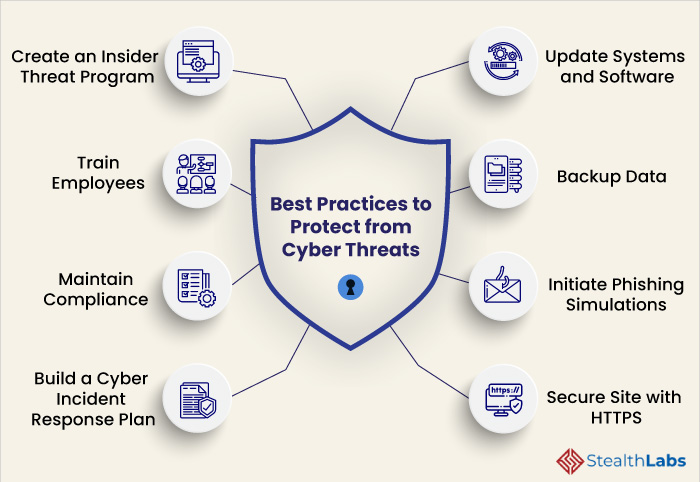
1) Create an Insider Threat Program
Creating an insider threat program is imperative for organizations to prevent employees from misusing their access privileges to steal or destroy corporate data. The IT security team should not delay and gain the approval of top management to deploy policies across departments.
2) Train employees
Employees are the first line of defense against cyberthreats for every organization. Thus, organizations must conduct comprehensive cybersecurity awareness programs to train employees on recognizing and responding to cyber threats. This dramatically improves an organization’s security posture and cyber resilience.
3) Maintain Compliance
Irrespective of the level of cybersecurity an organization implements, it must always maintain compliance with data regulations that apply to their industry and geographical location. The organization must stay abreast with the evolving compliance regulations to leverage the benefits it brings with it.
4) Build a Cyber Incident Response Plan
In the present digital era, no organization is exempt from cyberattacks. Thus, organizations of all sizes must build an effective Cyber Security Incident Response Plan (CSIRP) to navigate cyber adversaries. It enables businesses to prepare for the inevitable, respond to emerging threats, and recover quickly from an attack.
5) Regularly Update Systems and Software
As cyber threats are evolving rapidly, your optimized security network can become outdated within no time, putting your organization at the risk of cyberattack. Therefore, regularly update the security network and the associated systems and software.
6) Backup Data
Backing up data regularly helps reduce the risk of data breaches. Backup your website, applications, databases, emails, attachments, files, calendars, and more on an ongoing and consistent basis.
7) Initiate Phishing Simulations
Organizations must conduct phishing simulations to educate employees on how to avoid clicking malicious links or downloading attachments. It helps employees understand the far-reaching effects of a phishing attack on an organization.
8) Secure Site with HTTPS
Organizations must encrypt and secure their website with an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. HTTPS protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between the user and the website.
In Conclusion:

As reliance on digital technologies continues to increase, cyber attacks have become too sophisticated. Thus, organizations that rely on outmoded cybersecurity strategies leave themselves vulnerable to a potential cyberattack.
To prevent these threats, organizations must refine their cybersecurity program. An effective cybersecurity program can help organizations disrupt attacks as they occur, reduce recovery time, and contain future threats.
No matter what the level of your cybersecurity maturity, StealthLabs can help you fortify your security stance. With a flexible, practical, and proactive approach to cybersecurity, we can help you navigate the constantly evolving threat landscape.
More Cyber Security Articles:

