After years of hype and anticipation, the Internet of Things (IoT) has grown from a theoretical concept into mainstream business use-case.
The global number of IoT-connected devices is expected to reach 43 billion by 2023, almost 3x times more from 2018.
Internet of Things refers to a vast network of internet-connected devices that can communicate with other devices and networks. They can collect and analyze data and perform actions autonomously.
The adoption of IoT technology in business enhances functionality, increases productivity, reduces human errors, facilitates real-time monitoring, and improves customer experience, among others.
The number of businesses adopting IoT technologies has increased from 13% in 2014 to 25% in 2019.
Although many businesses have started investing in IoT technologies years ago, the automotive industry remains a major beneficiary of this latest wave of IoT maturity.

The automotive industry stood first in refining and redefining exiting technologies with IoT on par with the changing consumer preferences.
The advent of IoT in the automotive industry has opened new avenues for carmakers, especially when annual sales in automotive units remained almost constant since 2016.
IoT is helping automakers to develop a batch of next-generation vehicles, especially ‘Connected Cars‘.
While the automotive industry has traditionally focused on enhancing the vehicle’s internal functions, attention is now shifting towards connecting the car with the outside world and enhance the in-car experience.
Connected Cars: A Detailed Know How?
1. What is Connected Car?
2. Decades-Long Evolution of Connected Cars
3. How Do Connected Cars Work?
4. Connected vs Autonomous Vehicles – What’s the Difference?
5. What are the Benefits of Driving Connected Cars?
6. Challenges of Connected Cars
7. Global Connected Car Market Forecast
8. Connected Car Cybersecurity
9. How to Overcome Connected Car Security Challenges?
10. Tips to Improve Connected Car Security
11. Impact of 5G on Connected Cars
12. Conclusion
What is Connected Car?

A connected car is a vehicle that is equipped with onboard sensors and internet connectivity to interact with digital devices, road infrastructures and other vehicles.
The definition of ‘Connected Car’ is ever-changing as the connected car ecosystem is an ever-increasing collection of technologies.
At present, a connected car can be characterized as:
- A vehicle that facilitates communication between vehicle systems, driver and passenger devices, and external devices, networks and systems
- A vehicle that is inbuilt with the internet, Bluetooth and advancing ‘vehicle-to-vehicle’ communications technologies
- A vehicle that can access data, send data, download software, communicate with both internal and external IoT devices, and provide Wi-Fi facility.
The main goal of the connected car is to optimize its own operation, performance and maintenance, along with offering sophistication to users.
Decades-Long Evolution of Connected Cars

The concept of connected cars is not new. In fact, the first introduction to the connected cars technology came with General Motors’ OnStar in 1996. The primary purpose was to promote safety by triggering a cellular call to emergency call centers in case of accidents.
At first, OnStar could make only voice calls, but later began sending GPS location when cellular systems added data.
Within 20 years, connected cars facilitated safety, security, navigation, infotainment, diagnostics, and remote payment features to the users.
- Capabilities including vehicle health reports, turn-by-turn directions and network access device were introduced in 2003
- Data-only telematics was introduced in 2007
- Audi introduced 4G LTE Wi-Fi Hotspots in 2014
The connected cars infrastructure evolved very rapidly that, by 2015, OnStar had accepted 1 billion customer requests.
In fact, Gartner says that over 250 million connected cars will be produced, globally, by the end of 2020.
How Do Connected Cars Work?

Connected cars are integrated with an IoT network called CV2X (Cellular Vehicle to Everything) that connects vehicles, road infrastructure and other smart devices with each other.
Enhanced vehicle communication technologies facilitate fast data transmission and improve drivers’ response time.
The CV2X network is categorized into five types based on the vehicle’s communication with its surroundings. They are:
1) Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I)
V2I network refers to the interconnection of vehicles and the road infrastructure. The technology gathers information generated by the car and gives data about the road infrastructure to the driver.
The road infrastructure generally consists of lane markings, traffic lights, toll booths, petrol pumps, terminals, and diversions.
V2I technology facilitates information about safety, mobility, traffic flow, or environment-related conditions. It helps in avoiding traffic jams or long queues at petrol pumps or toll booths.
2) Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V)
The V2V technology facilitates communication between the vehicles in a proximate range through a wireless exchange of data. The exchanged data constitutes information related to position, speed and dynamics.
The primary purpose is to prevent accidents and ease traffic congestions.
3) Vehicle to Pedestrians (V2P)
V2P technology facilitates communication between the vehicle and pedestrians. It gathers information about the surrounding environment and communicates it to other vehicles, infrastructure and personal mobile devices.
A pedestrian can also connect the CV2X network using a mobile application to locate cabs and monitor transit timings.
The technology helps in improving safety and mobility on the road.
4) Vehicle to Network (V2N)
V2N technology enables interconnection between all types of vehicles and infrastructure systems, including cars, highways, subways, flyovers, ships, trains, and airplanes.
It also facilitates communication with the Intelligent Transport System (ITM) and weather forecast department to alert driver about weather conditions or road accidents.
With this technology, drivers can use voice commands to operate the GPS and music system of the vehicle while driving.
5) Vehicle to Cloud (V2C)
V2C technology facilitates vehicular communication with the broader Internet of Everything (IoE) via the cloud platform.
Here, the vehicle can communicate, interact and engage with other cloud-connected industries such as energy and transportation, infrastructure, devices, and smart homes.
Connected vs Autonomous Vehicles – What’s the Difference?

Connected Vehicles (CVs) and Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) are the trending technologies in the automotive industry, currently.
However, the difference between the technologies is often blurred.
Even though connected and autonomous vehicles are similar in so many ways, there are a few fundamental differences between them.
‘Level of driver involvement’ is the difference between the two cars.
Connected Cars
Connected cars deliver many novelty features including infotainment and productivity, and provides useful information to the driver to make safer and better decisions.
The connected car can facilitate remote parking and route guidance, but the driver still has ultimate control.
It simply supplies useful information to the driver and improves the abilities for cooperative driving. However, it doesn’t make any choices for the driver.
Autonomous Cars
In contrast to the connected vehicle, the autonomous vehicle can drive itself independently, without the need of a human driver. In a self-driving car, you will be in the passenger seat giving the car ultimate driving control.
It is computer-driven and has sensors, cameras, radar, and AI to negotiate public roads.
Without any human interference, it identifies other road users, avoids obstacles and takes the passengers to the destination using advanced image recognition.
What are the Benefits of Driving Connected Cars?

Connected car technology facilitates communication with the outside world, interaction with other vehicles, and real-time information on road, traffic and weather conditions.
Moreover, connected cars aim to tackle the most significant challenges encountered by the regular vehicles in the areas of safety, mobility and environment.
Connected Car Benefits
1) Safety
According to the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), 36,560 people died in road accidents in 2018. There were 4-5 million crashes in 2018 and the total road injury costs were estimated at USD 445.6 billion.
Connected car technologies facilitate the driver with all the information and tools to anticipate potential road accidents and significantly reduce the injuries and fatalities.
The vehicle gathers information about the objects on the road around it, including curbs, speed bumps and other vehicles, making it much easier to control the car.
NHTSA estimates that V2V and V2I technologies could eliminate or mitigate the severity of up to 80% of non-impaired crashes.
Owing to this enormous potential, the US Department of Transportation has already issued a proposed rule that mandates V2V communication on light vehicles in 2016.
2) Mobility
According to the Texas A&M Transportation Institute, an average commuter wasted nearly 7 full working days in an extra traffic delay, which accounted for over USD 1,000 in personal costs in 2017.
Connected car mobility software generates the most effective routes and enables the driver to make smart choices to avoid traffic jams, accidents, busy streets, or roads that are under construction.
3) Environment
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, around 142.23 billion gallons of finished motor gasoline were consumed in the US, an average of about 389.68 million gallons per day.
Connected car technology improves energy efficiency by providing real-time information to the customers to make “green” transportation choices.
4) Infotainment
Connected car technology enriches our journey with sophisticated infotainment systems that facilitate music, latest news, bulletins, films, chatting with friends, and information about the surroundings. The technology allows you to connect your smartphone with the car’s infotainment system.
5) Services
Connected cars enable service centers to conduct diagnosis and possibly prevent more invasive mechanical measures. Automakers can track data to assess the vehicle and develop more efficient vehicles.
Challenges with Connected Cars

1) Security
‘Security’ is one of the biggest concerns with connected cars.
As cars become more connected to the internet and systems, they can become more exposed to cybercriminals. Researches have already demonstrated how cybercriminals can take control of a connected car, forcing unintended braking, acceleration or steering. The hackers also have the opportunity to gain access to personal information through travel history and driving habits.
59% of car drivers in Brazil and Germany are afraid of possible system hacks when their car is connected to the internet.
2) Lack of Infrastructure
Connected cars can offer a host of benefits, but only when it is intrinsically connected to the infrastructure. So, the adoption of connected cars is directly dependent on the availability of sophisticated infrastructure.
Driving is not without challenges if the city is not well advanced.
3) Reliability
Reliability is another major challenge of a connected vehicle. There is a change that communication systems, network hardware and sensors may malfunction. The system has to deal with inaccurate data and faulty communications.
Global Connected Car Market Forecast
As per the market estimates, the globally connected car market size is projected to propel from USD 42.6 billion in 2019 to USD 212.7 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 22.3%.
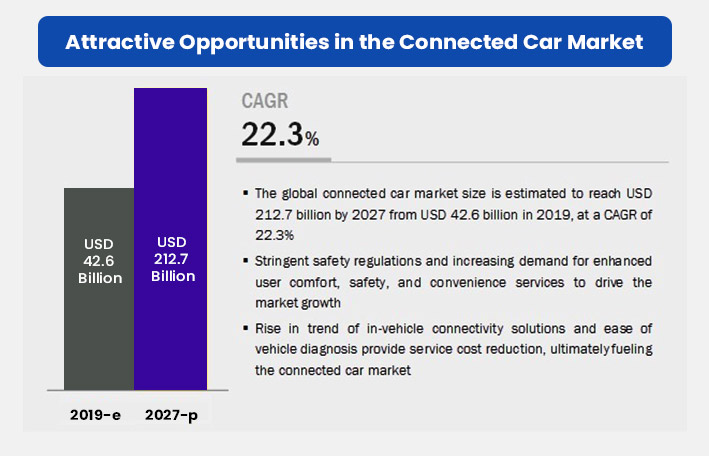
Source: MarketsandMarkets
High emphasis on road safety, the surge in consumer demand for in-vehicle connectivity, the advancement of IoT technologies and penetration of 5G technology are the prime factors that are expected to proliferate the demand in the global connected cars market during the forecast period 2019-27.
Autopilot Segment Growing at Alluring Rate
By service, the autopilot segment is expected to propel at the highest growth rate during the forecast period 2019-27. The growth of this segment is attributed to the safety and convenience features in the autopilot vehicle.
For instance, Tesla Model S uses sophisticated cameras and sensors to steer the vehicle, change lanes and adjust speeds automatically.
North America, Leading Connected Cars Market
By region, North America is considered to hold a significant share of the global cybersecurity market.
The dominance of North America can be attributed to the prevailing cutting-edge and compatible transit infrastructure, presence of major automobile manufactures and high tech-savvy population.
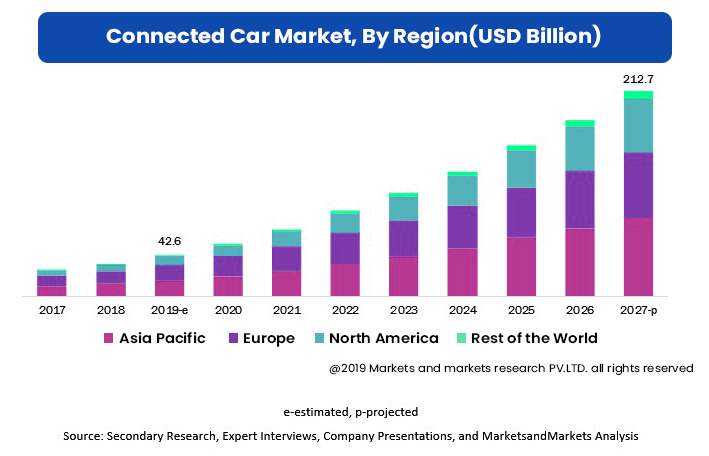
The entry of technological giants such as Google Inc and Apple Inc into the automotive industry has led to the growth of the connected cars market in North America.
General Motors, the pioneer of connected cars, is contributing to North America’s sheer affluence in the global connected cars market.
USA Connected Car Commerce
The US connected car commerce is projected to grow from a meager USD 2.25 billion in 2018 to a mammoth USD 16.43 billion by 2023, with a CAGR of 48.8%.
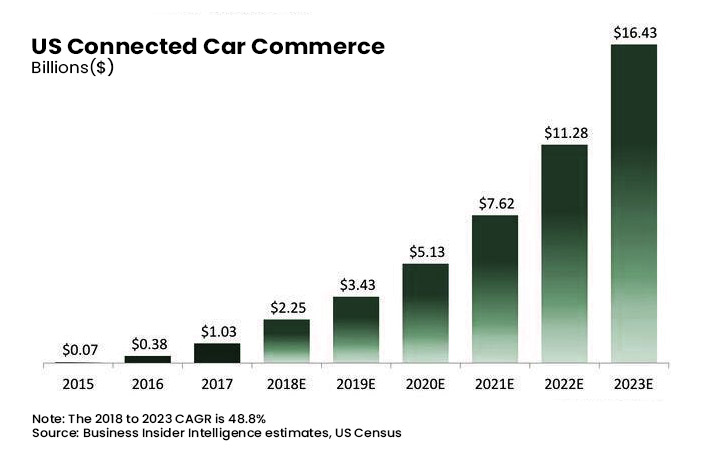
The emergence of autonomous vehicle technology is one of the critical factors proliferating the demand in the US connected car market.
The Intelligent Transportation Society of America is continually striving towards the renovation of the US transportation services by adopting technologies such as V2V and V2I communication. This, in turn, is creating sufficient demand driving the market.
Connected Car Cybersecurity

Even though connected cars offer a host of benefits, consumer privacy and security has become the primary concern for the automakers.
As vehicles become more connected to the internet, software vulnerabilities become easily accessible to cybercriminals to exploit the consumers.
Unauthorized access to the vehicle network or control of critical safety systems can cause a serious risk to the user’s personal information and also their physical safety.
Instances of Cybersecurity Risks in Connected Cars
- In 2015, two security researchers Charlie Miller and Chris Valasek demonstrated that they could hack a Chrysler jeep, taking over dashboard functions, steering, transmission and brakes. Consequently, Chrysler recalled 1.4 million vehicles to fix the bug.
- Two researchers Kevin Mahaffey and Marc Rogers demonstrated that they can remotely start the Tesla Model S car, drive it or cut its engine while someone else is driving.
- For nearly 5 years, millions of General Motors’ vehicles were vulnerable to a remote exploit that targeted the OnStar dashboard computer and track vehicles, engage brakes and control speed.
Thus, cybersecurity emerged as the need of the hour in the automotive industry.
It’s imperative for the automakers to adopt a cybersecurity approach that tackles not only the apparent exposures in the system but also the hidden vulnerabilities in the software.
Cyber Security Best Practices for Connected Vehicles

Issues pertaining to safety and security can act as a restraint for the connected car market. Automakers are obliged to follow the best cybersecurity practices to address software security risks in the connected vehicles.
1) Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
SAST is an essential tool to detect security risks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting and buffer overflow in the code. SAST or Static Analysis is a white box method of testing that helps identify vulnerabilities in the initial stages of development.
So, developers can resolve issues quickly without breaking builds or passing on vulnerabilities to the final release of the application.
SAST takes place during the early stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
2) Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
IAST technique helps in analyzing code for security vulnerabilities while the app is run by using dynamic testing techniques. It reports vulnerabilities in real-time, eliminating the need for extra time in your CI/CD pipeline.
IAST takes place during the test/QA stage of SDLC.
3) Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
With the rise in open source use in automotive software, automakers must track components to address open source issues and vulnerabilities.
Code audits revealed that open source components make up 25% of any given automotive application.
SCA solution helps secure risk management of open-source use throughout the software supply chain, allowing the security team to discover and track open source vulnerabilities.
4) Code Risk Management
It’s imperative for the automakers to manage code risk effectively. Integrating processes and automated techniques into the system software solutions help in maintaining the security and code quality of automotive software applications and platforms.
How to Overcome Connected Car Security Challenges?

With an estimated 250 million connected cars expected on the road by 2020, the connected car presents a lucrative opportunity for the automotive market.
However, there are many speculations on the potential security risk associated with connected cars.
In need of the hour, automakers are adopting various security solutions to reassure the end-use that all precautions are being taken against cybersecurity threats.
Also Read: Autonomous Car Security: Adversarial Attacks Against New Mobility!
3 Tips to Improve Connected Car Security

1) End-to-End Security
Adequate cybersecurity and data privacy are imperative for successful automotive telematics. The automakers should have enough expertise in network and infrastructure security. They should integrate security measures at every access point.
End-to-end data security implementation secures all channels and backend infrastructure.
2) Data Integrity
Carmakers should ensure that data and information produced and gathered by the vehicle is stored in its raw state. So, in cases of a privacy breach, the original data can be restored quickly. It’s imperative to maintain the integrity of the data collected apart from protecting it.
3) Information Availability
The connected car manufacturers should ensure that all the systems of the vehicle facilitate high information scalability and availability. Systems should be monitored regularly to achieve a high level of service without any interruption.
Impact of 5G on Connected Cars

Even though 5G technology is still a work in progress in the automotive industry, the pace of development and deployment is proliferating.
As per the market estimates, the share of connected cars that are actively connected to a 5G service is projected to increase from 15% in 2020 to 74% by 2023, reaching 94% in 2028.
5G technology is becoming the future of connected cars with its lucrative capabilities including high-bandwidth, low latencies, network slicing, and high data speeds.
The next-generation technology can enhance the connected car’s ability to interact with its environment, both in and outside the vehicle.
Benefits of 5G in Connected Cars

1) Collision Avoidance
The prime benefit of 5G technology is the increase of collision avoidance in connected cars by facilitating high speed, reliable exchange of data between vehicle, infrastructure and environment.
Owing to the low latency of 5G, the external monitoring systems can transmit large data packets within 10 milliseconds, facilitating fast response.
2) Improved In-car Monitoring
5G technology improves the responsiveness of in-car monitoring sensors and components. So, the components can instantly detect and respond to unexpected incidents like driver falling asleep or other distractions.
3) Enhanced Customer Experience
Under 5G, connected cars not only make traveling safe but also more enjoyable. The 5G real-time connectivity transforms the connected car into a collaborative, digital environment. Connected cars have the potential to become mobile workspaces.
Moreover, 5G introduces a new level of entertainment and productivity into the driving experience.
4) Improved Consumer Confidence
A recent Deloitte survey revealed that nearly 50% of consumers doubt the safety of autonomous vehicles. However, 5G enables reliable, instant responses to internal and external threats, making the connected car safer.
The surveys predict that there will be 41 million 5G-connected cars on the road by 2030, rising to 83 million by 2035, as 5G networks become more pervasive.
Conclusion
Introduced at the end of the previous century, connected car technology propelled with the rapid advancement of technologies including IoT, AI and ML.
Every technological innovation in the automotive ecosystem is meant to enhance safety, optimize routing, decrease pollution, and improve accessibility.
Facilitating all the aspects above, connected cars are set to become a common phenomenon across the world within no time. The connected cars will be fully integrated into our digital lives, just like smartphones and computers. All in all, we will be gliding through the cities as passengers rather than drivers.
Stay tuned to Stealth Labs for more information security updates!
More Articles:


